Events are serialised and coded in a standardised format for sending and receiving between modules. In addition, a packet containing multiple different types of events is segmented by event-type such that a search can quickly retrieve events of only a specific type. The packet is formed as such:
Each event class defines the TAG used to identify itself and also the method with which the event data is serialised. Managing the serialisation and de-serialisation of the event data is then simply a case of using the event class to write/read its TAG and then call its encode/decode functions on the serialised data. The eventdriven::vBottle class handles the coding of packets in the event-driven project.
Events are defined in a class hierarchy, with each child class calling its parent encode/decode function before its own. Adding a new event therefore only requires defining the serialisation method for any new data that the event-class contains (e.g. the Flow event only defines how the velocities are encoded and calls its parent class, the AdressEvent, to encode other information, such as position and timestamp).
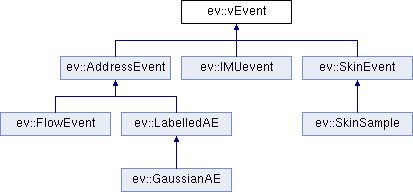
Event Coding Definitions
The vEvent uses 4 bytes to encode a timestamp (T)
An AddressEvent uses 4 bytes to encode position (X, Y), polarity (P) and channel (C). Importantly, as AddressEvent is of type vEvent the timestamp information of this event is always encoded as well.
or, if the VLIB_10BITCODEC CMake flag is set ON (used for the ATIS camera) the AddressEvent is encoded as:
A FlowEvent uses 8 bytes to encode velocity (ẋ, ẏ), each 4 bytes represent a float. Similarly as FlowEvent is of time AddressEvent the FlowEvent also encodes all the position and timestamp information above.
A LabelledAE is labelled as belonging to a group ID (I) using a 4 byte int.
A GaussianAE extends a cluster event with a 2 dimensional Gaussian distribution parameterised by (sx, sy, sxy) using a total of 12 bytes.
Coding in YARP
The eventdriven::vBottle class wraps the encoding and decoding operations into a yarp::os::Bottle such that an example vBottle will appear as:
NOTE: The actual data sent by YARP for a bottle includes signifiers for data type and data length, adding extra data to the bottle as above.
 1.8.13
1.8.13